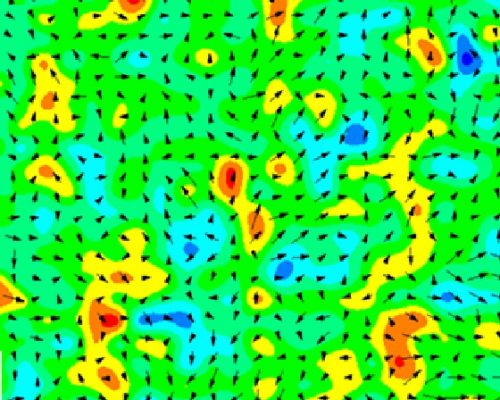
Researchers from Jožef Stefan Institute (Electronic Ceramics Department), National Institute of Chemistry, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Materials Center Leoben and Tokyo Institute of Technology published a study in Nature Communications entitled “Atomic scale symmetry and polar nanoclusters in the paraelectric phase of ferroelectric materials” (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23600-3).
Using an atomic-resolution study by aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy complemented by Raman spectroscopy, they directly reveal, visualize, and quantitatively describe static 2-4 nm large polar nanoclusters in the nominally nonpolar cubic phases of barium titanate based ceramics. These results have implications for understanding the atomic-scale structure of disordered materials and may help clarify ambiguities about the dynamic-versus- static nature of nano-sized clusters.