Excellent in Science is the annual project of the Slovenian Research Agency for science promotion. In 2017, the achievement “Interpretation of electric conductivity of domain walls in bismuth ferrite” was also recognized as excellent. The work was presented by Asst. Prof. dr. Andreja Bencan Golob.
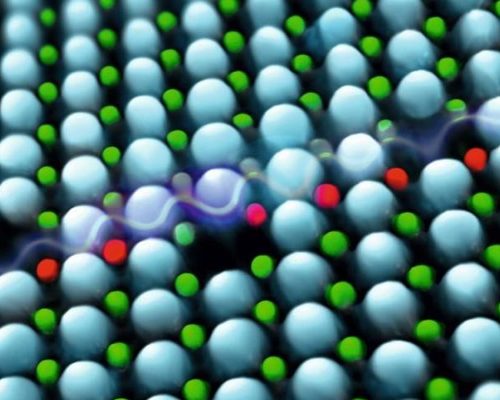
Figure: Schematic representation of point defects on the domain wall in bismuth ferrite (Tadej Rojac and co-authors, Nature Materials, 2016)
Ferroelectric bismuth ferrite is being extensively studied as a candidate material for high-temperature piezoelectric devices. The drawback for practical utilization is its high electrical conductivity which mostly stems from local conduction at the domain walls. The accumulation of mobile charged defects to screen the polarization charges at the domain walls has been proposed as the origin of such local conduction in several ferroelectrics, however, the presence of defects has not yet been directly confirmed. Researchers from Jozef Stefan Institute and National Institute of Chemistry, in collaboration with colleagues from Switzerland and Japan (T. Rojac, A. Bencan, G. Drazic, N. Sakamoto, H. Ursic, B. Jancar, G. Tavcar, M. Makarovic, J. Walker, B. Malic in D. Damjanovic) , were the first to identify accumulation of charged defects at domain walls in ferroelectric BiFeO3. This finding explains the p-type hopping conduction at the domain walls in BiFeO3 and thus represents the missing piece for explaining the intriguing electrical properties of domain walls in ferroelectrics.
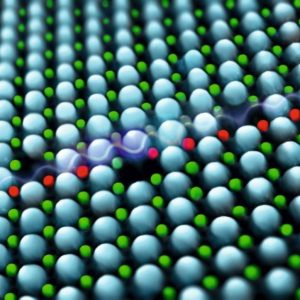
Figure: Point defects at the domain wall in bismuth ferrite (Tadej Rojac et al., Nature Materials, 2016)